Need trainer @ Koenig Solutions Ltd for Virtualization technology (VMware and Citrix) for location Delhi, Bangalore, Dubai and Goa. Interested people can write to us info@koenig-solutions.com with latest profile, candidate must have strong communication skills along with technical knowledge !!!!
Tuesday, December 4, 2012
VMware Job Opening With Koenig Solutions Ltd (www.koenig-solutions.com)
Need trainer @ Koenig Solutions Ltd for Virtualization technology (VMware and Citrix) for location Delhi, Bangalore, Dubai and Goa. Interested people can write to us info@koenig-solutions.com with latest profile, candidate must have strong communication skills along with technical knowledge !!!!
Monday, December 3, 2012
vCenter Server Appliance 5.1 Configuration
I am writing this article as I got few queries, that while they deploy appliance for vCenter 5.1 there is some issue with SSO and then vCenter service is not coming up.
So in this case I can advice one thing, once your vCenter Appliance deployment completed then power on the same, before connecting to the Web Based interface to do initial configuration configure the hostname and ip address, DNS etc, to do that connect to console of vCenter Appliance VM and then login to the appliance. Once logon after that you need to run the script given at below mentioned path:-
/opt/vmware/share/vami/vami_config_net
this will give you the choice to do hostname, ip addess, dns, gateway etc config options.
once you confirm that all the configuration is correct. Then you can restart the appliance.
Once appliance is back, now you can
https://IPorName:5480
and then logon to appliance with user root and password as you configure and then do the initial setup to make the vCenter Service up and running.
So in this case I can advice one thing, once your vCenter Appliance deployment completed then power on the same, before connecting to the Web Based interface to do initial configuration configure the hostname and ip address, DNS etc, to do that connect to console of vCenter Appliance VM and then login to the appliance. Once logon after that you need to run the script given at below mentioned path:-
/opt/vmware/share/vami/vami_config_net
this will give you the choice to do hostname, ip addess, dns, gateway etc config options.
once you confirm that all the configuration is correct. Then you can restart the appliance.
Once appliance is back, now you can
https://IPorName:5480
and then logon to appliance with user root and password as you configure and then do the initial setup to make the vCenter Service up and running.
Friday, October 19, 2012
Masking a LUN from ESX and ESXi using the MASK_PATH plug-in
Caution: This procedure only applies to LUNs that are being managed by the VMwre NMP multipathing service. If you are using 3rd party multipathing plugin such as Powerpath/VE then LUNs must be excluded from the 3rd party multipathing software and put under NMP control before they can be masked again properly.
To mask a LUN from ESX/ESXi 4.x and ESXi 5.0 using the MASK_PATH plug-in:
Note: Any differences in the commands between ESX/ESX 4.x and ESXi 5.0 will be noted with the version of ESX/ESXi before the command.
Note: You may still see a single path to the LUN on one or more storage adapters after following the steps in this article. This disappears after the ESX host is rebooted. As long as the datastore is no longer visible, no issues are being reported in the logs, and rescans are completing in a timely fashion, the residual path can be safely ignored.
Source:- http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=1009449
To mask a LUN from ESX/ESXi 4.x and ESXi 5.0 using the MASK_PATH plug-in:
Note: Any differences in the commands between ESX/ESX 4.x and ESXi 5.0 will be noted with the version of ESX/ESXi before the command.
- Log into a console or SSH session on your host. For more information, see Using Tech Support Mode in ESXi 4.1 and ESXi 5.0 (1017910).
- Look at the Multipath plug-ins currently installed on your ESX with the command:
# esxcfg-mpath -G
The output indicates that there are, at a minimum, 2 plug-ins: The VMware Native Multipath plug-in (NMP) and the MASK_PATH plug-in (ESXi 5.0 will only show the NMP plugin by default), which is used for masking LUNs. There may be other plug-ins if third-party software (such as EMC PowerPath) is installed. For example:
# esxcfg-mpath -G
MASK_PATH
NMP - List all the claimrules currently on the ESX with the command:
ESXi 5.0: # esxcli storage core claimrule list
ESX/ESXi 4.x: # esxcli corestorage claimrule list
There are two MASK_PATH entries: one of class runtime and the other of class file.
The runtime is the rules currently running in the PSA. The file is a reference to the rules defined in/etc/vmware/esx.conf. These are identical, but they could be different if you are in the process of modifying the/etc/vmware/esx.conf.
Note: There is already a rule of vendor=DELL model=Universal Xport. This means that pseudo or management LUNs with these attributes are masked from the ESX.
The output from the command is similar to:
Rule Class Type Plugin Matches
0 runtime transport NMP transport=usb
1 runtime transport NMP transport=sata
2 runtime transport NMP transport=ide
3 runtime transport NMP transport=block
4 runtime transport NMP transport=unknown
101 runtime vendor MASK_PATH vendor=DELL model=Universal Xport
101 file vendor MASK_PATH vendor=DELL model=Universal Xport
65535 runtime vendor NMP vendor=* model=* - Add a rule to hide the LUN with the command:
ESXi 5.0: # esxcli storage core claimrule add --rule <number> -t location -A <hba_adapter> -C <channel> -T <target> -L <lun> -P MASK_PATH
ESX/ESXi 4.x: # esxcli corestorage claimrule add --rule <number> -t location -A <hba_adapter> -C <channel> -T <target> -L <lun> -P MASK_PATH
The parameters -A <hba_adapter> -C <channel> -T <target> -L <lun> define a unique path. You can leave some of them unspecified if the LUN is uniquely defined. The value for parameter --rule can be any number between 101 and 200 that does not conflict with a pre-existing rule number from step 3.
Note: For a detailed command description, see esxcli corestorage Command-Line Options and vSphere Command-Line Interface Installation and Scripting Guide.
This is a brief example of usage:- Find the naa device of the datastore you want to unpresent with the command:
# esxcfg-scsidevs -m
naa.600508b1001037383941424344450300:3 /vmfs/devices/disks/naa.600508b1001037383941424344450300:3 4b44572e-8a1c74b2-42d4-00237dde59b8 0 datastore1
naa.600601604550250018ea2d38073cdf11:1 /vmfs/devices/disks/naa.600601604550250018ea2d38073cdf11:1 4bb21500-dc941493-2904-00237dde59ba 0 DatastoreToMask - Check all of the paths that the naa device has:
# esxcfg-mpath -b -d naa.600601604550250018ea2d38073cdf11
vmhba33:C0:T3:L0 state:active Local HBA vmhba33 channel 0 target 3
vmhba33:C0:T2:L0 state:standby Local HBA vmhba33 channel 0 target 2
vmhba33:C0:T1:L0 state:active Local HBA vmhba33 channel 0 target 1
vmhba33:C0:T0:L0 state:standby Local HBA vmhba33 channel 0 target 0 - As you apply the rule -A vmhba33 -C 0 -L 0, verify that there is no other device with those parameters. You can use the wildcard vmhba33:C0.*L0 (. means any character and * means zero or more times).
# esxcfg-mpath -L | egrep "vmhba33:C0.*L0"
vmhba33:C0:T3:L0 state:active naa.600601604550250018ea2d38073cdf11 vmhba33 0 3 0 NMP active san iqn.1998-01.com.vmware:cs-tse-h42-17d4ba81 00023d000001,iqn.1992-04.com.emc:cx.ckm00092300229.b2,t,4
vmhba33:C0:T2:L0 state:standby naa.600601604550250018ea2d38073cdf11 vmhba33 0 2 0 NMP standby san iqn.1998-01.com.vmware:cs-tse-h42-17d4ba81 00023d000001,iqn.1992-04.com.emc:cx.ckm00092300229.a3,t,3
vmhba33:C0:T1:L0 state:active naa.600601604550250018ea2d38073cdf11 vmhba33 0 1 0 NMP active san iqn.1998-01.com.vmware:cs-tse-h42-17d4ba81 00023d000001,iqn.1992-04.com.emc:cx.ckm00092300229.b3,t,2
vmhba33:C0:T0:L0 state:standby naa.600601604550250018ea2d38073cdf11 vmhba33 0 0 0 NMP standby san iqn.1998-01.com.vmware:cs-tse-h42-17d4ba81 00023d000001,iqn.1992-04.com.emc:cx.ckm00092300229.a2,t,1 - Add a rule for this LUN with the command:
ESXi 5.0: # esxcli storage core claimrule add --rule 192 -t location -A vmhba33 -C 0 -T 0 -L 0 -P MASK_PATH
ESX/ESXi 4.x: # esxcli corestorage claimrule add --rule 192 -t location -A vmhba33 -C 0 -T 0 -L 0 -P MASK_PATH
Notes:- For more information about the adapter, channel, target and LUN values, see Identifying disks when working with VMware ESX (1014953).
- For more information about the command and its options, see Managing Claim Rules with esxcli corestorage claimrule in the vSphere Command-Line Interface Documentation.
- Find the naa device of the datastore you want to unpresent with the command:
- Verify that the rule is in effect with the command:
ESXi 5.0: # esxcli storage core claimrule list
ESX/ESXi 4.x: # esxcli corestorage claimrule list
The output indicates our new rule. It is only of class file. You must then load it into the PSA.
For example:
Rule Class Type Plugin Matches
0 runtime transport NMP transport=usb
1 runtime transport NMP transport=sata
2 runtime transport NMP transport=ide
3 runtime transport NMP transport=block
4 runtime transport NMP transport=unknown
101 runtime vendor MASK_PATH vendor=DELL model=Universal Xport
101 file vendor MASK_PATH vendor=DELL model=Universal Xport
192 file location MASK_PATH adapter=vmhba33 channel=0 target=* lun=0
65535 runtime vendor NMP vendor=* model=* - Reload your claimrules with the command:
ESXi 5.0: # esxcli storage core claimrule load
ESX/ESXi 4.x: # esxcli corestorage claimrule load - Re-examine your claimrules and verify that you can see both the file and runtime class. Run the command:
ESXi 5.0: # esxcli storage core claimrule list
ESX/ESXi 4.x: # esxcli corestorage claimrule list
For example:
Rule Class Type Plugin Matches
0 runtime transport NMP transport=usb
1 runtime transport NMP transport=sata
2 runtime transport NMP transport=ide
3 runtime transport NMP transport=block
4 runtime transport NMP transport=unknown
101 runtime vendor MASK_PATH vendor=DELL model=Universal Xport
101 file vendor MASK_PATH vendor=DELL model=Universal Xport
192 runtime location MASK_PATH adapter=vmhba33 channel=0 target=* lun=0
192 file location MASK_PATH adapter=vmhba33 channel=0 target=* lun=0
65535 runtime vendor NMP vendor=* model=* - Unclaim all paths to a device and then run the loaded claimrules on each of the paths to reclaim them.
Note: Unclaiming disassociates the paths from a PSA plugin. These paths are currently owned by NMP. You need to dissociate them from NMP and associate them to MASK_PATH.
Run the command:
ESXi 5.0: # esxcli storage core claiming reclaim -d naa.id
ESX/ESXi 4.x: # esxcli corestorage claiming reclaim -d naa.id
Where naa.id is the naa ID used in step 3. This device is the LUN being unpresented. This command attempts to unclaim all paths to a device and runs the loaded claimrules on each of the paths unclaimed to attempt to reclaim them.
For example:
ESXi 5.0: # esxcli storage core claiming reclaim -d naa.600601604550250018ea2d38073cdf11
ESX/ESXi 4.x: # esxcli corestorage claiming reclaim -d naa.600601604550250018ea2d38073cdf11 - Verify that the masked device is no longer used by the ESX host.
If you are masking a datastore, perform one of these options:- Connect the vSphere Client to the host and click Host > Configuration > Storage, then click Refresh. The masked datastore does not appear in the list.
- Rescan the host by navigating to Host > Configuration > Storage Adapters > Rescan All.
- Run the command:
# esxcfg-scsidevs -m
The masked datastore does not appear in the list.
To see all the masked LUNs use the command:
# esxcfg-scsidevs -c
To verify that a masked LUN is no longer an active device, run the command:
# esxcfg-mpath -L | grep naa.id
For example:
# esxcfg-mpath -L | grep 600601604550250018ea2d38073cdf11
Empty output indicates that the LUN is not active. - Connect the vSphere Client to the host and click Host > Configuration > Storage, then click Refresh. The masked datastore does not appear in the list.
Note: You may still see a single path to the LUN on one or more storage adapters after following the steps in this article. This disappears after the ESX host is rebooted. As long as the datastore is no longer visible, no issues are being reported in the logs, and rescans are completing in a timely fashion, the residual path can be safely ignored.
Source:- http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=1009449
vSphere 5.1 Release Notes !
vSphere 5.1 is there now:-
This is really great to a have quick look on vSphere 5.1 Release Notes, I took few product support notes from:-
Product Support Notices
- vSphere Client. In vSphere 5.1, all new vSphere features are available only through the vSphere Web Client. The traditional vSphere Client will continue to operate, supporting the same feature set as vSphere 5.0, but not exposing any of the new features in vSphere 5.1.vSphere 5.1 and its subsequent update and patch releases are the last releases to include the traditional vSphere Client. Future major releases of VMware vSphere will include only the vSphere Web Client.For vSphere 5.1, bug fixes for the traditional vSphere Client are limited to security or critical issues. Critical bugs are deviations from specified product functionality that cause data corruption, data loss, system crash, or significant customer application down time where no workaround is available that can be implemented.
- VMware Toolbox. vSphere 5.1 is the last release to include support for the VMware Tools graphical user interface, VMware Toolbox. VMware will continue to update and support the Toolbox command-line interface (CLI) to perform all VMware Tools functions.
- VMI Paravirtualization. vSphere 4.1 was the last release to support the VMI guest operating system paravirtualization interface. For information about migrating virtual machines that are enabled for VMI so that they can run on later vSphere releases, see Knowledge Base article 1013842.
- Windows Guest Operating System Customization. vSphere 5.1 is the last release to support customization for Windows 2000 guest operating systems. VMware will continue to support customization for newer versions of Windows guests.
- VMCI Sockets. Guest-to-guest communications (virtual machine to virtual machine) are deprecated in the vSphere 5.1 release. This functionality will be removed in the next major release. VMware will continue support for host to guest communications.
Thursday, October 11, 2012
Committing snapshots when there are no snapshot entries in the Snapshot Manager
See below KB 1002310 article from vmware for fixing this problem.
http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=1002310
http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=1002310
Friday, September 28, 2012
Rename Virtual Machine After Creating VMware vSphere
Renaming virtual Machine inventory name is much easier, just
right click and rename. But in the datastore all the folder and files related
to that VM keep the old name, means if you have VM with inventory name “VM001”
then in the datastore this will create the folder “VM001” and within that folder
all the files also start with same name like see the diagram below
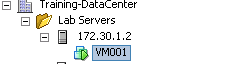
Then suppose you rename the VM in the inventory VM001à db-srv-del-01 after this you can see that in the inventory you have new name but in the datastore folder and files still keep the old name. See the screen shot below:-
So if you want to apply the new name to all the files and folder related to that VM, you need to shutdown the VM and then remove from inventory and then manually rename all the files and folder with new name and then add back to inventory. For details on that see below:-
Shutdown the VM and then remove from inventory.
After that connect to the console of esxi/esx
server and then change directory to datastore where that VM is located. Like
in my example that VM is located in datastore Private02 and the folder name is
VM001. I just enabled SSH in my esxi server and then connect using the Putty to
esxi host. So that I can reach those files, perform the steps as in
the screenshot :-
After renaming the folder, you need to
rename all the files also, so do the steps as in screenshot:-
Once all the related files are renamed with new name, after that you need to modify the vmx file to point to the new name of vmdk, so edit vmx file with any editor, I used in this case vi and then rename the .vmdk name to new name .vmdk and save the file and exit.
After this you also need to update the
.vmdk fiel to point to new –flat.vmdk.
so you need to edit the vmname.vmdk file with vi editor (or any editor
you feel comfortable), and modify the name of –flate.vmdk to new name –flat.vmdk
after this save and exit.
Once all this done now your VM is ready with new name, now you can go back to vSphere client and browse your datastore and then locate the VM name folder and then locate .vmx file and add back to inventory. Once added to inventory you can power on the VM and now all files and folder related to that VM have new name.
Monday, August 20, 2012
VMWARE VIRTUAL DISK FORMATS
VMWARE VIRTUAL DISK FORMATS
Three types of virtual disks
are available to VMs in vSphere. You should become familiar with all of them,
including their similarities, differences, weaknesses, and strengths.
THICK VIRTUAL
DISK
The thick virtual disk is the
traditional virtual disk format that most of us have deployed with most of our
VMs. This format pre-allocates the capacity of the virtual disk from the
datastore at the time it is created. This format does not format the VMDK at
the time of deployment. This means that data that needs to be written must
pause while the blocks required to store the data are zeroed out. The operation
occurs on demand any time an area of the virtual disk that has never been
written to is required to store data.
Figure 5) A
thick VMDK as it relates to storage blocks on an array.

THIN VIRTUAL
DISK
The thin virtual disk is very
similar to the thick format, with the exception that it does not preallocate
the capacity of the virtual disk from the datastore when it is created. When
storage capacity is required, the VMDK allocates storage in chunks equal to the
size of the file system block. For VMFS, this is from 1MB through 8MB (size
selected at deployment), and for NFS it is 4KB. The process of allocating
blocks on a shared VMFS datastore is considered a metadata operation and as
such executes SCSI locks on the datastore while the allocation operation is executed.
Although this process is very brief, it does suspend the write operations of
the VMs on the datastore.
Figure 6) A
thin VMDK as it relates to storage blocks on an array.
Similar to the thick format,
thin VMDKs are not formatted at the time of deployment. Therefore, data that
needs to be written must pause while the blocks required to store the data are
zeroed out. The process of allocating blocks from within the datastore occurs
on demand any time a write operation attempts to store data in a block range
inside the VMDK that has not been written to by a previous operation.
To summarize the zeroing out
and allocation differences between a thick and thin virtual disk, just remember
that both suspend I/O when writing to new areas of disk that need to be zeroed.
However, before this can occur with a thin virtual disk, it might also have to
obtain additional capacity from the datastore.
EAGER-ZEROED
THICK VIRTUAL DISK
The eager-zeroed thick virtual
disk is similar to the thick format because it preallocates the capacity of the
virtual disk from the datastore when it is created. However, unlike the thick
and thin formats, an eager-zeroed thick virtual disk actually formats all of
its data blocks at the time of deployment. This virtual disk format does not
include or require the allocation and zeroing on-demand processes.
Figure 7) An
eager-zeroed thick VMDK as it relates to storage blocks on an array.
Tuesday, August 14, 2012
VMware vSphere 5 Memory Management and Monitoring diagram
The VMware vSphere 5 Memory Management and Monitoring diagram provides a comprehensive look into the ESXi memory management mechanisms and reclamation methods. This diagram also provides the relevant monitoring components in vCenter Server and the troubleshooting tools like ESXTOP,
Source:-
http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=2017642
Source:-
http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=2017642
Monday, August 6, 2012
Thursday, July 12, 2012
Understanding VM Snapshot
See the link below for how snapshot works and it effect your current state of Virtual Machine..
http://vmfootprints.org/understanding-snapshot
On this link there is a link to download presentation download and see this, really informative and helpful to understand the snapshot concept.
http://vmfootprints.org/understanding-snapshot
On this link there is a link to download presentation download and see this, really informative and helpful to understand the snapshot concept.
Wednesday, July 11, 2012
Cloud Computing Private, Public and Hybrid
Public cloud:
In Public cloud the computing infrastructure is hosted
by the cloud vendor at the vendor’s premises. The customer has no visibility and
control over where the computing infrastructure is hosted. The computing
infrastructure is shared between any organizations (sharing the infrastructure).
Private cloud:
The computing infrastructure is dedicated to a
particular organization and not shared with other organizations. Some experts
consider that private clouds are not real examples of cloud computing. Private
clouds are more expensive and more secure when compared to public clouds.
Private clouds are of two types:
- On-premise private clouds and externally hosted private clouds.
- Externally hosted private clouds are also exclusively used by one organization, but are hosted by a third party specializing in cloud infrastructure. Externally hosted private clouds are cheaper than On-premise private clouds.
Hybrid cloud
Organizations may host critical applications on private clouds and applications with relatively less security concerns on the public cloud. The usage of both private and public clouds together is called hybrid cloud. A related term is Cloud Bursting. In Cloud bursting organization use their own computing infrastructure for normal usage, but access the cloud for high/peak load requirements. This ensures that a sudden increase in computing requirement is handled gracefully.
Tuesday, July 10, 2012
Auditing ESXi Shell logins and commands in ESXi 5.x (History of executed commands in ESXi)
ESXi maintains a history of all commands entered in the ESXi Shell. This shell command history is maintained in the
shell.logfile. Within the transcription of commands, the command issuer is identified only by the process or world ID, rather than by username or client address. This article describes how to correlate authentication information from the auth.log file with the history of commands executed in the ESXi Shell.
For more information on the locations of the log files described, see Location of ESXi 5.0 log files (2004201) and Location of log files for VMware products (1021806).
Procedure
To determine the commands executed in the ESXi Shell, and which user and client issued the request:
- Obtain access to the
auth.logandshell.loglog files.- Log in to the ESXi Shell, and open each log using the
lesscommand. - Use a web browser to access
https://ESXiHostnameOrIP/host/auth.logandhttps://ESXiHostnameOrIP/host/shell.log. - Use the
vifscommand line utility in the vCLI to copy the logs to a client, and review them there. - Read the files from within a
vm-supportlog bundle.
- Log in to the ESXi Shell, and open each log using the
- Open the log file
/var/log/auth.login a text viewer. - Identify the authentication record, including the Username, Timestamp, and World ID for the session:
- ESXi Shell login at the console appears similar to:
2011-08-29T18:01:00Z login[64386]: root login on 'char/tty/1' - ESXi Shell login via interactive SSH appears similar to:
2011-08-29T18:01:00Z sshd[12345]: Connection from 10.11.12.13 port 26052011-08-29T18:01:00Z sshd[12345]: Accepted keyboard-interactive/pam for root from10.11.12.13 port 2605 ssh22011-08-29T18:01:00Zsshd[64386]: Session opened for 'root' on /dev/char/pty/t02011-08-29T18:01:00Zsshd[12345]: Session closed for 'root' on /dev/char/pty/t0
...
2011-08-29T18:35:05Z sshd[12345]: Session closed for 'root' 2 - ESXi Shell login via SSH with public key appears similar to:
2011-08-29T18:01:00Z sshd[12345]: Connection from 10.11.12.13 port 26052011-08-29T18:01:00Z sshd[12345]: Accepted publickey for root from 10.11.12.13 port 2605ssh22011-08-29T18:01:00Zsshd[64386]: Session opened for 'root' on /dev/char/pty/t02011-08-29T18:01:00Zsshd[12345]: Session closed for 'root' on /dev/char/pty/t0
...
2011-08-29T18:35:05Z sshd[12345]: Session closed for 'root' 2
Each of these authentication records indicate a successful authentication for the userrooton August 29th at 18:01 GMT. The SSH methods also include the IP address tha the connection was initated from. The shell session is being handled by world64386. - ESXi Shell login at the console appears similar to:
- Close the log file
/var/log/auth.log. - Open the log file
/var/log/shell.login a text editor or viewer. - Identify commands entered which contain the same World ID as identified in Step 3, appearing similar to:
2011-08-29T18:01:01Zshell[64386]: Interactive shell session started2011-08-29T18:05:02Zshell[64386]: cd /var/log2011-08-29T18:05:03Zshell[64386]: ls2011-08-29T18:13:04Zshell[64386]: vmware -v2011-08-29T18:35:05Zshell[64386]: exit
Since the commands were entered in the console session handled by world ID64386, we know that they correspond to the authentication session established by userrootas described in Step 3.
Sunday, June 24, 2012
Enabling FT on VM under nested ESXi 5 host
Note:- this article is Only for test and learning purpose not for production...
Then you need three row replay.supported true replay.allowBTOnly true, replay.allowFT true after adding this it look like see the snap below:-
After adding the rows you can click ok and then again ok, now if all other requirement of FT are configured you can enable the FT on VM even this is running on nested esxi host.
Saturday, June 23, 2012
Virtual Machine Swap file size (.vswp)
Swap File Size Calculation
Every VM have some amount of Memory configured. So when we power on the VM, vmkernel have to create the Swap file for VM (this file is different file than vmdk file), so that in case of memory contention overallocated memory can be delivered (in the storage there must be free space available to create that file otherwise we can't power on the VM).
Swap File is calculated using the below formula:-
Allocated Memory to VM - Reserve Memory to VM = Size of Swap file (.vswp)
Suppose VM is configure with 2048 MB of Memory and Reserve for that VM is 512 MB then swap file size is 1536 MB as per above formula:-
2048 - 512 = 1536 MB.
Even you reserve 100 % allocated memory to VM swap file still created but with 0KB in size.
Swap file created even you have enough memory on host, but vmkernel only use this file (in case of memory contention) if demand of memory is more than the available amount of Memory on Host (ESXi).
Host Profile
What is Host Profile ?
The host
profiles feature creates a profile that encapsulates the host configuration and
helps to manage the host configuration, especially in environments where an
administrator manages more than one host or cluster in vCenter Server.
Host
profiles eliminates per-host, manual, or UI-based host configuration and
maintains configuration consistency and correctness across the datacenter by
using host profile policies. These policies capture the blueprint of a known, validated reference host
configuration and use this to configure networking, storage, security, and
other settings on multiple hosts or clusters. You can then check a host or
cluster against a profile’s configuration for any deviations.
How to Use Host Profile ?
You perform
host profiles tasks in a certain workflow order.
You must
have an existing vSphere installation with at least one properly configured
host.
- Set up and configure the host that will be used as the reference host.
- A reference host is the host from which the profile is created.
- Create a profile using the designated reference host.
- Attach a host or cluster to the profile.
- Check the host's compliance to the reference host's profile. If all hosts are compliant with the reference host, they are correctly configured.
- Apply the host profile of the reference host to other hosts or clusters of hosts (Host need to be in maintenance mode to apply the profile).
Note:- Using host profiles is only supported
for VMware vSphere 4.0 hosts or later
Creating a
Host Profile
You create a
new host profile by using the designated reference host's configuration.
A host
profile can be created from:
- Host Profile main view
- Host's context menu
Create a Host Profile from Host Profiles
View
You can
create a host profile from the Host Profiles main view using the configuration
of an existing host.
Prerequisites
You must
have a vSphere installation and at least one properly configured host in the
inventory.
Procedure
1 In the
Host Profiles main view, click Create Profile.The Create Profile wizard appears.
2 Select the
option to create a new profile and click Next.
3 Select the
host you want to designate as the reference host for the new host profile and
click Next.
The reference host must be a valid host.
4 Type the
name and enter a description for the new profile and click Next.
5 Review the
summary information for the new profile and click Finish to complete creating
the
profile. The new profile appears in the
profile list.
Create a Host Profile from Host
You can
create a new host profile from the host's context menu in the Hosts and
Clusters inventory view.
Prerequisites
You must
have a vSphere installation and at least one properly configured host in the
inventory.
Procedure
1 In the
Host and Clusters view, select the host that you want to designate as the
reference host for
the
new host profile. The host must be a valid host to use as a reference host.
2
Right-click the host and select Host Profile > Create Profile from Host
The Create Profile from Host wizard opens.
3 Type the
name and enter a description for the new profile and click Next.
4 Review the
summary information for the new profile and click Finish to complete creating
the
profile. The new profile appears in the
host's Summary tab.
Attach Profiles from the Host
Before you
can apply the profile to a host you need to attach the host to the profile or
the profile to the host. You can attach a profile to a host from the host's
context menu in the Hosts and Clusters inventory view. When a host profile is
attached to a cluster, the host or hosts within that cluster are also attached
to the host profile. However, when the host profile is detached from the
cluster, the association between the host or host within the cluster and that
host profile remain.
Procedure
1 In the
Host and Clusters view, select the host to which you want to attach a profile.
2
Right-click the host and select Host Profile > Manage Profile.
NOTE
If no host profiles exist in your inventory, a dialog appears asking if
you want to create
and attach the host to this profile.
and attach the host to this profile.
3 In the
Attach Profile dialog, select the profile to attach to the host and click OK.
The host profile is updated in the Summary tab
of the host.
Apply a Profile from the Host
You can
apply a profile to a host from the host's context menu.
Prerequisites
The host
must be in maintenance mode before a profile is applied to it.
Procedure
1 In the
Host and Clusters view, select the host to which you want to apply a profile.
2 Right-click
the host and select Host Profile > Apply Profile.
3 In the
Profile Editor, enter the parameters and click Next.
4 Continue
until all the required parameters are entered.
5 Click
Finish.
Compliance
Status is updated.
For more details:-
http://pubs.vmware.com/vsphere-50/topic/com.vmware.ICbase/PDF/vsphere-esxi-vcenter-server-50-host-profiles-guide.pdf
For more details:-
http://pubs.vmware.com/vsphere-50/topic/com.vmware.ICbase/PDF/vsphere-esxi-vcenter-server-50-host-profiles-guide.pdf
Wednesday, June 20, 2012
How to change Virtual
Machine Snapshot files location (vSphere 5)
I have taken an example, I have created two datastore like below:-
VM-Datastore dedicated for VM related files like vmx,vmdk etc
Snapshot-Datastore dedicated for VM
Snapshot files like vmsn, delta.vmdk etc.
If you want to change the snapshot files location for different
datastore than default, you need to shut down the VM first. Then remove the VM
from inventory, and then use esxi Local Shell or SSH Shell and edit the .vmx
file of that VM with vi editor and add the lines at the end of the file:-
Snapshot.redoNotWithParent
= “true”
workingDir = “Location of your datastore” like see the snapshot below:-
After this save the file and add the VM to inventory back using the vSphere client. When you power on the VM, and after this you will take snapshot the snapshot, files will created under the defined datastore. You can browse and confirm the snapshot file are under the new datastore like:-
So now snapshot files location is as per your requirement.
How to change Virtual
Machine swap file location VMware ESXi
I have taken an example, I have created two datastore like below:-
VM-Datastore dedicated for VM related files like vmx,vmdk
etc
Swap-Datastore dedicated for VM Swap files.
If you want to change the swap file location to different datastore than default, you need to shut down the VM first. Once VM is offline then go to Edit Setting of that VM and then click on Options tab like see the screenshot below:-
Then click on Configure Parameters button. Then you’ll get another window like below and then you need to click on add row button :-
Under the name filed you need to type “sched.swap.dir” and in the value field you need to type the path of datastore where you want swap files. Like in my case I have dedicated datastore for Swap files, so I have defined the path “/vmfs/volumes/Swap-Datastore” and the click on OK
After that when you powered in that VM the swap file get
created under new datastore. You can browse and confirm thenswap file is under
this like:-
So now swap file location is as per your requirement.
Tuesday, June 19, 2012
Security and the
Virtualization Layer (esxi)
VMware designed the virtualization layer, or VMkernel, to
run virtual machines. It controls the hardware that hosts use and schedules the
allocation of hardware resources among the virtual machines. Because the VMkernel
is fully dedicated to supporting virtual machines and is not used for other
purposes, the interface to the VMkernel is strictly limited to the API required
to manage virtual machines.
ESXi provides additional VMkernel protection with the
following features:
Memory Hardening
The ESXi kernel, user-mode applications, and executable
components such as drivers and libraries are located at random, non-predictable
memory addresses. Combined with the non-executable memory protections made available
by microprocessors, this provides protection that makes it difficult for
malicious code to use memory exploits to take advantage of vulnerabilities.
Kernel Module
Integrity
Digital signing ensures the integrity and authenticity of
modules, drivers and applications as they are loaded by the VMkernel. Module
signing allows ESXi to identify the providers of modules, drivers, or
applications and whether they are VMware-certified.
Trusted Platform
Module(TPM)
Each time ESXi boots, it measures the VMkernel and a subset
of the loaded modules (VIBs) and stores the measurements into Platform
Configuration Register (PCR) 20 of the TPM. This behaviour is enabled by
default and cannot be disabled. Hardware support for this feature is fully
tested and supported by VMware and its OEM partners.
NOTE:- Not all VIBs are measured as part of this
process.
The VMware TPM/TXT feature that leverages the fully tested
hardware support is suitable for a proof-of-concept that demonstrates
monitoring of certain TPM PCR values, by alerting when any values change from
one boot to the next. Third-party solutions could use this feature to detect
changes to VIB measurements stored in these PCRs for the following cases:
- Corruption of the measured images
- Unexpected or unauthorized updates, or other types of changes to themeasured images
For more details you can see:-
Monday, June 18, 2012
New virtual machine capabilities (vSphere 5)
ESXi 5.0 introduces a new generation of virtual hardware with virtual machine hardware version 8, which includes the following new features:-
- 32-way virtual SMP. ESXi 5.0 supports virtual machines with up to 32 virtual CPUs, which lets you run larger CPU-intensive workloads on the VMware ESXi platform.
- 1TB of virtual machine RAM. You can assign up to 1TB of RAM to ESXi 5.0 virtual machines.
- Software support for 3D graphics to run Windows Aero. ESXi 5.0 supports nonhardware accelerated 3D graphics to run Windows Aero and Basic 3D applications in virtual machines.
- USB 3.0 device support. ESXi 5.0 features support for USB 3.0 devices in virtual machines with Linux guest operating systems. USB 3.0 devices attached to the client computer running the vSphere Web Client or the vSphere Client can be connected to a virtual machine and accessed in it. USB 3.0 devices connected to the ESXi host are not supported.
- UEFI virtual BIOS. Virtual machines running on ESXi 5.0 can boot from and use the Unified Extended Firmware Interface (UEFI).
Friday, June 15, 2012
Resource Pool
Management (vSphere5)
You can create, manage and delete the Resource Pool, While
you are managing stand-alone host esxi (before adding to vCenter Server). Once
you add host to vCenter Server after that Resource pool management is only
using vCenter, direct connection to host (esxi) do not allow resource pool
management, until you remove host (esxi)
from vCenter inventory.Monday, June 11, 2012
VMware Certified Associate Level free till 31 Jan 2014 ! Don't Miss !
Wait till next promotion !!
Meanwhile if not yet completed, you can go for VCA (VMware Certified Associate) exams for free !
VMware Certified Associate certification is available now for all the who have attended VMware vSphere Training program, or even who have the vmware product knowledge and want to have some recognition to that, You can go for the VCA certification.
So hurry up add some more certification to profile.
Good Luck !
100% free voucher till 31 January 2014
Promotion Code:- VMRT8B34585F
Exam Voucher VCP510
So many of you have attended the training for VMware vSphere: Install Configure Manage [5.x], even some of you are already VCP5, so congrates to becoming VCP and welcome to VCP community, those who are yet preparing for exam or not find time to take the exam. There is exam voucher available for VCP510 you can get 25% discount on your exam total cost.
VM029B2D3E3C
This voucher is valid till 31st October 2013
Take the exam soon and become VCP. Good Luck for your exam.
Meanwhile if not yet completed, you can go for VCA (VMware Certified Associate) exams for free !
VMware Certified Associate certification is available now for all the who have attended VMware vSphere Training program, or even who have the vmware product knowledge and want to have some recognition to that, You can go for the VCA certification.
· VCA-DCV - vSphere: Install, Configure, Manage [5.1] supported by Fundamentals e-Learning - VMware Data Center Virtualization Fundamentals &VMware Data Center Virtualization Fundamentals (Japanese)
· VCA-WM - Horizon View: ICM AND Horizon Mirage, each supported by Fundamentals e-Learning - VMware Workforce Mobility Fundamentals&VMware Workforce Mobility Fundamentals (Japanese)
· VCA-Cloud - vCloud Automation Center: ICM, supported by Fundamentals e-Learning - VMware Cloud Fundamentals & VMware Cloud Fundamentals (Japanese)So hurry up add some more certification to profile.
Good Luck !
100% free voucher till 31 January 2014
Promotion Code:- VMRT8B34585F
Exam Voucher VCP510
So many of you have attended the training for VMware vSphere: Install Configure Manage [5.x], even some of you are already VCP5, so congrates to becoming VCP and welcome to VCP community, those who are yet preparing for exam or not find time to take the exam. There is exam voucher available for VCP510 you can get 25% discount on your exam total cost.
VM029B2D3E3C
This voucher is valid till 31st October 2013
Take the exam soon and become VCP. Good Luck for your exam.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)


















